Difference between revisions of "Vallegrande Speak"
m (tidy) |
|||
| (87 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{DISPLAYTITLE:Old Vela Luka | + | {{DISPLAYTITLE:Old Vela Luka Speak}} |
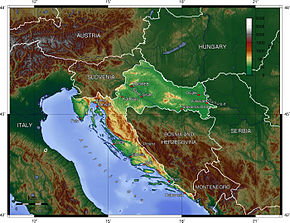
| − | [[File:250px-Croatia-Dalmatia-1.jpg|thumb|right|400px|The island of Korcula is marked red. | + | [[File:250px-Croatia-Dalmatia-1.jpg|thumb|right|400px|The island of Korcula is marked red. Dalmatia (the dark purple) within todays modern [[Croatia]] ]] |
| − | ''' | + | '''Old Vela Luka Speak''' in Croatian, ''Staro Luški govor'' <ref>Tako su stari govorili. Translated: ''That's how the old folk use to speak''.</ref> (or |
| + | alternatively it could be called Vallegrande Speak) is an old [[Korcula Dialect]] from the small town of Vela Luka. The town is on the west end of the island of Korčula.<ref>The č is pronounced ''ch''.</ref> The island of Korčula lies just off the Dalmatian coast in [[Croatia]].<ref>John Everett-Healu. "Dalmatia." Concise Dictionary of World Place-Names. Oxford University Press. 2005. Encyclopedia.com</ref> The language base of this Korčula Dialect is '''Croatian Chakavian''' <ref>'''Editors note''': Slavic tribes invaded the region of''' Roman Dalmatia''' in the early Middle Ages. Prior to the arrival of the Slavs, Roman Dalmatia was mainly inhabited by a '''Roman Latin-Illyrian''' population. Recent DNA studies have stated that more than three quarters of today's Croatian men are the descendants of Europeans who inhabited Europe 13 000-20 000 years ago (prior to the arrival of the Slavs). The first primary source (factual-that its authenticity isn't disputed) to mention the Croatian (Hrvat) identity in the Balkans was '''Duke Branimir''' (Latin:'' "Branimiro comite dux cruatorum cogitavit"'' c. 880 AD). Branimir was a Slav from Dalmatia.</ref> (it is also intermixed with Old Western Shtokavian<ref>[http://ukpmc.ac.uk/articles/PMC2121596/reload=0;jsessionid=7BE5888928AF51ECB79DC33089D0E57A.jvm1 The Land of 1000 Islands] by Igor Rudan | ||
| − | * "However, the clashes between the [[Directory:Turkey|Ottoman Empire]] and Venetian Republic produced extensive migrations from the mainland areas, especially from today's Bosnia and Herzegovina, to the eastern parts of the islands of Brač, Hvar, Korčula, and Pag [Dalmazia Veneta]. The newcomers brought their gene pool and a variety of cultural specificities, including the Shtokavian dialect of the Croatian language to the predominantly “Chakavian” area. The most extensive migrations to these islands occurred during the Cypriote (1571-1573), Candian (1645-1669), and Morean wars (1684-1699)."</ref>). It has | + | * "However, the clashes between the [[Directory:Turkey|Ottoman Empire]] and Venetian Republic produced extensive migrations from the mainland areas, especially from today's Bosnia and Herzegovina, to the eastern parts of the islands of Brač, Hvar, Korčula, and Pag [Dalmazia Veneta]. The newcomers brought their gene pool and a variety of cultural specificities, including the Shtokavian dialect of the Croatian language to the predominantly “Chakavian” area. The most extensive migrations to these islands occurred during the Cypriote (1571-1573), Candian (1645-1669), and Morean wars (1684-1699)."</ref>). It has very strong elements of ''Italian Venetian'' and it also has small remnants of the extinct Romance (Latin) language, '''Dalmatian''' <ref>PRILOG PROUČAVANJU LEKSIČKIH RAZLIKA IZMEĐU GOVORA BLATA I VELE LUKE (I) by Petar Milat Panža ''(Eng:'' Contribution to the Study of Lexical Differences Between the Speech of Blato and Vela Luka): ''..... a famous Croatian linguist finally asserted that there is no Slavic studies without Roman studies! He admitted that it is not possible to study the Croatian language with its three dialects - Štokavian, Kajkavian and Chakavian - without studying Romance influences, especially on our Chakavian languages. By the term Romanic influences, we understand remnants from Latin through Dalmatian (Old Dalmatian, Dalmatian-Romance), then remnants from Venetian and all other Italian dialects, and finally the influences of the standard Italian language. Another group worthy of research is the lexicon of Slavic origin, which appears in the speech of Vela Luka, but is not present in the speech of Blato.'' |
| − | + | </ref><ref>'''Encyclopedia Britannica''' {{quote| | |
| + | ''Romance language formerly spoken along the Dalmatian coast from the island of Veglia (modern Krk) to Ragusa (modern Dubrovnik). Ragusan Dalmatian probably disappeared in the 17th century.}} | ||
| + | </ref><ref>[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dalmatian_language Dalmatian Language (Wikipedia)]</ref>. The Dalmatian remnants within the dialect have been sometimes referred to as Corzulot. The local dialect is sometimes referred to as 'Naški' <ref>'''Note''': Naški means 'ours' thus meaning ''"our language"'' in Croatian.</ref> (the '''š''' is pronounced '''sh'''). | ||
| − | + | The island was from 1420 to 1797 part of the '''Republic of Venice''' (the French Empire dissolved the Republic <ref>Note: In old Venetian 'Repùblega Vèneta' also know as La Serenissima </ref> in 1797). The Old-Slavic term was Krkar. According to Antun (Antonio) Rosanovic written in his [[Defence of Korcula (part two)|Defence of Korcula in 1571]] the Greeks named it ''Corcyra Melena''.<ref>Greek: Kórkyra Melaena or Κόρκυρα Μέλαινα, and Corcyra Nigra (Latin)</ref> | |
| + | One of Korčula's older names was Curzola. Vela Luka in the past was called Vallegrande (Latin: vallem maximam). | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:242424 1862049509067 689609 o.jpg|thumb|right|500px|A ''Vela Luka-Vallegrande'' postcard from 1903, written in Croatian and [[Italy|Italian]]. Photo taken by Ernesto Furlani.]] | ||
| − | |||
===Chronology-Korcula Island Languages=== | ===Chronology-Korcula Island Languages=== | ||
* Illyrian (Delmatae) | * Illyrian (Delmatae) | ||
* Greek | * Greek | ||
* Latin (Romans) | * Latin (Romans) | ||
| − | * Romance Dalmatian (Latin) | + | * Romance Dalmatian (Vulgar Latin) |
| − | * | + | * Croatian (Slavic Chakavian) |
* Venetian (Romance language) | * Venetian (Romance language) | ||
| − | * Old Shtokavian - Slavic | + | * Old West Shtokavian - Slavic |
| − | * Italian (standardise language arrived) | + | * Italian (standardise language arrived, besides Latin) |
| − | * | + | * Croato-Serbian (Slavic standardise language<ref>Standardise Croatian arrived in the late 1850s. The Standardise language was referred to as '''Illyrian''' (Illirski). Ref from Osnovna Škola "Vela Luka" Vela Luka Zbornik-150 Godina Školstva u Velaoj Luci, p.50 written in Croatian</ref> ''also'' known as Serbo-Croatian, based on Neo Štokavian<ref>[//books.google.com.au/books?id=_lNjHgr3QioC&pg=PA132&lpg=PA132&dq=Croatian+Identity&source=bl&ots=fD7ElNqJfQ&sig=b_VK71LL4FYXG7LBjfPVUCSVC-E&hl=en&sa=X&ei=eSClVOSxLuLWmAW484HYDQ&ved=0CEAQ6AEwBzgK#v=onepage&q=Croatian%20Identity&f=false Language and Identity in the Balkans: Serbo-Croatian and Its Disintegration ... By Robert D. Greenberg]</ref>) |
Modern times | Modern times | ||
* Croatian (Croatian Literary Standard, standardise language) | * Croatian (Croatian Literary Standard, standardise language) | ||
| − | ==Words from the | + | ==Words from the Old Vela Luka Dialect - Staro Luški== |
| − | + | Old Vela Luka Dialect - '''English''' - Croatian | |
{{col-begin}} | {{col-begin}} | ||
{{col-break}} | {{col-break}} | ||
| Line 33: | Line 39: | ||
* adojat - to please (aldojat: meaning in Romance Dalmatian ''to feel at home, to be settled'') | * adojat - to please (aldojat: meaning in Romance Dalmatian ''to feel at home, to be settled'') | ||
* afitat - rent ('''Venetian Italian''': afìt) | * afitat - rent ('''Venetian Italian''': afìt) | ||
| − | * aimemeni ''or'' | + | * aimemeni ''or'' aime meni - poor me ''or'' oh dear, dear me |
* alavia - done properly ''or'' it's Ok!, just right - u redu (Romance Dalmatian ''just right'') | * alavia - done properly ''or'' it's Ok!, just right - u redu (Romance Dalmatian ''just right'') | ||
| − | * apoteka - pharmacy (Venetian: apoteca, Greek: Apotheke) | + | * apoteka - pharmacy (Venetian: apoteca, '''Greek''': Apotheke) |
* arbol - ship's mast | * arbol - ship's mast | ||
* aria - air - zdrak (Venetian: aria) | * aria - air - zdrak (Venetian: aria) | ||
| Line 66: | Line 72: | ||
* bobon - lolly | * bobon - lolly | ||
* boca - bottle - flaša (Venetian: boca) | * boca - bottle - flaša (Venetian: boca) | ||
| − | * bome - of course - naravno (Romance Dalmatian) | + | * bome - of course - naravno (Romance Dalmatian: bome) |
* bonaca - the sea is dead calm (Venetian: bonàça) | * bonaca - the sea is dead calm (Venetian: bonàça) | ||
* botilja - bottle ('''Romance Dalmatian''': ''botaila'') | * botilja - bottle ('''Romance Dalmatian''': ''botaila'') | ||
| Line 120: | Line 126: | ||
* fratar - brother - brat (Romance Dalmatian) | * fratar - brother - brat (Romance Dalmatian) | ||
* frigati - to fry (Romance Dalmatian: fregur) | * frigati - to fry (Romance Dalmatian: fregur) | ||
| − | * frižul - a spot to have a chat ( | + | * '''frižul''' - a spot to have a chat, on a stone bench <ref>''''Da Se Ne Zaboravi''': Rječnik, Stare Priče, Običaji i Zanati u Blatu na Otoku Korčuli' ''by'' Žanetić Pudarić, Blato 2009 (''Eng:'' Let's Not Forget: Dictionary, Old Stories, Customs and Trades in Blato on the Island of Korcula) |
| + | . In Croatian, meaning taken from the book: ''"ižul - niska kamena klupa uz kuću koja služi za odmaranje, ćakulu, za prtit stoku, itd (a low stone bench next to the house that is used for resting, discussions ....., etc."''</ref> (Romance Dalmatian: faul ''or'' faular, meaning to speak) | ||
* forca - power (apply with strength) | * forca - power (apply with strength) | ||
* fortuna - strong wind | * fortuna - strong wind | ||
| Line 154: | Line 161: | ||
* katrida - chair - stolica (Romance Dalmatian: '' katraida'') | * katrida - chair - stolica (Romance Dalmatian: '' katraida'') | ||
* katun - corner (Latin: cantus) | * katun - corner (Latin: cantus) | ||
| − | * '''klapa''' - an a cappella form of music <ref>The traditional '''Klapa''' was composed of around half of dozen male singers (in recent times there are ''female'' Klape groups). Klapa singing dates back centuries. The arrival of the Slavic-Croatians to Dalmatia and their subsequent settlement in the area, began the process of the cultural mixing of Slavic culture with that of the traditions of the Roman population of Dalmatia. This process was most evident in the coastal and island regions of Dalmatia. In the 19th century a standard form of Klapa singing emerged. Church music heavily influences the arrangements. The modern Klapa style was established in the 1960s.</ref> (Venetian:clapa ''"singing crowd"'') | + | * '''klapa''' - an a cappella form of music <ref>The traditional '''Klapa''' was composed of around half of dozen male singers (in recent times there are ''female'' Klape groups). Klapa singing dates back centuries. The arrival of the Slavic-Croatians to Dalmatia and their subsequent settlement in the area, began the process of the cultural mixing of Slavic culture with that of the traditions of the Roman population of Dalmatia. This process was most evident in the coastal and island regions of Dalmatia. In the 19th century a standard form of Klapa singing emerged. Church music heavily influences the arrangements. The modern Klapa style was established in the 1960s.</ref> (Venetian: clapa ''"singing crowd"'') |
* keleh - the floor | * keleh - the floor | ||
* kolbuk - hat | * kolbuk - hat | ||
| Line 195: | Line 202: | ||
* Ma ''or'' mat - mother - majka | * Ma ''or'' mat - mother - majka | ||
* mećat - to throw | * mećat - to throw | ||
| − | * meja - a stone wall in the field ( | + | * meja - a stone wall in the field (drystone fence, Ita: muretto a secco) |
* mezo - in between (Venetian: mèzo ''"half"'') | * mezo - in between (Venetian: mèzo ''"half"'') | ||
* Mi povidamo na našu ''or'' Mi pripovidamo na našu- Mi pričamo naš jezik (in neoshtokavian) | * Mi povidamo na našu ''or'' Mi pripovidamo na našu- Mi pričamo naš jezik (in neoshtokavian) | ||
| Line 236: | Line 243: | ||
* prat- wash | * prat- wash | ||
* pule - baby donkey | * pule - baby donkey | ||
| − | * punte - | + | * punte - points |
* punistra - window (Latin: fenestra) | * punistra - window (Latin: fenestra) | ||
| − | * puntižel - | + | * puntižel - plank, board |
* reful - small strong wind ''a gust'' | * reful - small strong wind ''a gust'' | ||
* regeta - light sheet metal | * regeta - light sheet metal | ||
| Line 244: | Line 251: | ||
* ritko - not often | * ritko - not often | ||
* roba - clothes - odjeća | * roba - clothes - odjeća | ||
| + | * rotunda - circular dry stone building - vrtujak | ||
* sak - bag (Venetian: saco) | * sak - bag (Venetian: saco) | ||
* senjat - to mark | * senjat - to mark | ||
| Line 292: | Line 300: | ||
* vala - bay'' (vale - bays)'' | * vala - bay'' (vale - bays)'' | ||
* vapor - ferry - trajekt (Venetian: Bapor meaning ''steamship'') | * vapor - ferry - trajekt (Venetian: Bapor meaning ''steamship'') | ||
| − | * vara vamo - move on ''or'' move over there | + | * vara vamo - move on ''or'' move over there, these are commands ''for'' local donkeys when on the move |
| − | * vedro - clear sky | + | * vedro - clear sky (Romance Dalmatian: vedar - ''to see'') |
* vesta - dress - ženska haljina (Venetian: garment, vestir: dress) | * vesta - dress - ženska haljina (Venetian: garment, vestir: dress) | ||
* '''vela''' - big - veliko | * '''vela''' - big - veliko | ||
* vida - screw | * vida - screw | ||
* Vi ga niste vidili - You did not see him. | * Vi ga niste vidili - You did not see him. | ||
| + | * vlasi - hair - kosa | ||
* volja - desire, wanting too, mood - želja (Venetian: wish, desire, Can be used i.e. Nije mi volja. Meaning - I'm not in the mood ''or'' I'm not feeling too good. | * volja - desire, wanting too, mood - želja (Venetian: wish, desire, Can be used i.e. Nije mi volja. Meaning - I'm not in the mood ''or'' I'm not feeling too good. | ||
* zamantan - crazy - lud | * zamantan - crazy - lud | ||
| Line 315: | Line 324: | ||
We can definitely confirm that from the 13th century onwards there were '''two ethnic''' communities living on the island in the middle ages <ref>[http://books.google.com.au/books?id=p3oGybOY1w4C&pg=PA103&dq=korcula+Venice++Slavs&hl=en&ei=oMBjTJPQBoicvgPkpPCeCg&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=6&ved=0CE4Q6AEwBQ#v=onepage&q=korcula%20Venice%20%20Slavs&f=false When Ethnicity Did not Matter in the Balkans:] by John Van Antwerp Fine. (p103) {{quote| | We can definitely confirm that from the 13th century onwards there were '''two ethnic''' communities living on the island in the middle ages <ref>[http://books.google.com.au/books?id=p3oGybOY1w4C&pg=PA103&dq=korcula+Venice++Slavs&hl=en&ei=oMBjTJPQBoicvgPkpPCeCg&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=6&ved=0CE4Q6AEwBQ#v=onepage&q=korcula%20Venice%20%20Slavs&f=false When Ethnicity Did not Matter in the Balkans:] by John Van Antwerp Fine. (p103) {{quote| | ||
| − | ''In 1262 the Venetian praised the Slavs and Latins on the island of Korcula for submitting to the prince Venice had sent.'' }}</ref><ref>Smiciklas, ''CD'' V, (p237)</ref><ref>N. Klaic, ''Povijest Hrvata u Razvijenom'', ( | + | ''In 1262 the Venetian praised the Slavs and Latins on the island of Korcula for submitting to the prince Venice had sent.'' }}</ref><ref>Smiciklas, ''CD'' V, (p237)</ref><ref>N. Klaic, ''Povijest Hrvata u Razvijenom'', (p83) </ref>, one being descendants of the Roman Empire and the other being of Slavic descent. |
| − | Two languages became the norm on the island, firstly the Romance Latin language called ''Dalmatian'' | + | Two languages became the norm on the island, firstly the Romance Latin language called ''Dalmatian'', then we have the '''arrival''' of old Slavic [[Croatia|Croatian Chakavian]] language. With time these languages started to overlap with a form of '''bilingualism''' being created (with the written language being [[Latin]]). The fact that Slavs from the old neighbouring [[Directory:Croatia|Kingdom of Croatia]] also spoke old Slavic Chakavian could indicate that this group of Slavs came from the same ''or'' similar tribal group. |
| − | When the Serbian forces were annihilated in the ''Battle of Kosovo'' by the [[Directory:Turkey|Ottoman Empire]] (دولت عليه | + | When the Serbian forces were annihilated in the ''Battle of Kosovo'' by the [[Directory:Turkey|Ottoman Empire]] (Ottoman Turkish: دولت عليه عثماني) in '''1389''' a large group of peoples started a exodus westward (Byzantine's Constantinople fell to the Ottoman Empire - Turks in 1453). Venetian Dalmatia (Dalmazia Veneta) started to acquire new people in its region (i.e., Eastern Croatians - Hercegovci, Montenegrins, Albanians, Serbs & others) and add to the fact that the Black Plague <ref>Korcula was devastated by the plague in 1529 and 1558.{{citeweb|url=http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/322146/Korcula|title='''"Korcula."''' '''Encyclopædia Britannica'''. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encyclopædia Britannica, 2011. Tue. 8 Mar. 2011. |date=[[2011]]|accessdate=2011-03-8}} |
| − | * '''Encyclopædia Britannica''': " A plague devastated the town in 1529, depleting the population. The burned houses of infected persons, called kućišta..."</ref><ref>[http://books.google.com.au/books?id=ZyOYDrSkX80C&pg=PA239&dq=Italian+population+Curzola&hl=en&ei=3ptXTcqwOIjSuwPI3NyrBQ&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=1&ved=0CDAQ6AEwADgK#v=onepage&q=Italian%20population%20Curzola&f=false The Shores of the Adriatic (Illustrated Edition)] by F Hamilton Jackson (p239)</ref> depleted the island's population the Venetian authorities saw a need to bring new families to the island of Korčula. Amongst these were Western Shtokavian Slavic speakers. With these new added migrations the Slavic speakers became a majority | + | * '''Encyclopædia Britannica''': " A plague devastated the town in 1529, depleting the population. The burned houses of infected persons, called kućišta..."</ref><ref>[http://books.google.com.au/books?id=ZyOYDrSkX80C&pg=PA239&dq=Italian+population+Curzola&hl=en&ei=3ptXTcqwOIjSuwPI3NyrBQ&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=1&ved=0CDAQ6AEwADgK#v=onepage&q=Italian%20population%20Curzola&f=false The Shores of the Adriatic (Illustrated Edition)] by F Hamilton Jackson (p239)</ref><ref>Plague Epidemic on the Island of Korcula 2007 by Nikola Bačić 2007: " ''13. EPIDEMIC 1617. It swept all of Dalmatia, but left the most severe consequences on the island of Korčula. It appeared first with the sailors of the Venetian ship (as N. Ostojić describes) who wintered in Korčula that year. Suburban homes had to be emptied to turn into dwellings for diseased sailors. The contagion soon spread to citizens and within a few months more than half of the population had died. A particularly devastating disease was, according to the data, for wealthier residents, so many entire noble families who had a reputation for their homeland were extinct.''"</ref> depleted the island's population the Venetian authorities saw a need to bring new families to the island of Korčula. Amongst these were Western Shtokavian Slavic speakers. With these new added migrations the Slavic speakers became a strong majority. This applies more to west end of the island, with the village of Račišće being the exception (the village is in the eastern part of the island). |
| − | If the translation of the [[Defence of Korcula|Defence of Korčula]]
from Ottoman Turkish | + | If the translation of the [[Defence of Korcula|Defence of Korčula]]
from Ottoman Turkish Attack in 1571 (Corcyrae Melenae Opus - Antonii Rosanei), originally written by Antun (Antonio) Rozanovic is ''untainted'', we can see that the majority of the defenders of the island were by 1571 of Slavic decent. If we use this as a reference, then from the mid 16th century onwards the majority of Korčula's population was indeed of Slavic origins. |
| − | === | + | ===Old Vela Luka Dialect Evolved Late 18th Century=== |
| − | Vela Luka's first beginnings, are from the late 17th century (late 1600s). It started with the population of the neighbouring Blato <ref>In Croatian blato means ''mud'' it also has been said the word is related to ''water'' referring to the once lake in neighbouring field</ref> setting up a town in the large bay of Vallegrande | + | Vela Luka's first beginnings as a town, are from the late 17th century (late 1600s). It started with the population of the neighbouring Blato <ref>In Croatian blato means ''mud'' it also has been said the word is related to ''water'' referring to the once lake in neighbouring field</ref> setting up a town with a port in the large bay of Vela Luka (Vallegrande ''or'' Latin: vallem maximam). Zvonko Maričić (Maricich) states in the late 1500s there where already five buildings in the bay (one being a church). The buildings belong to Ismaelli, Gabrielli, Canavelli<ref> In re-written modern Croatian: Kanavelić</ref> and Kolovic. |
| − | Then around the 1690s <ref>Vela Luka od 1490 do 1834 ''by'' Zvonko Maričić (p207)</ref> there were additional twelve households (written in modern Croatian): Draginić, Tulić, Nalošić, Kostričić, Cetinić, | + | Then around the 1690s <ref>Vela Luka od 1490 do 1834 ''by'' Zvonko Maričić (p207)</ref> there were additional twelve households (written in modern Croatian): Draginić, Tulić, Nalošić, Kostričić, Cetinić, Mirošević, [[Directory:Zuvela|Žuvela]], Prižmić, Marinović, Dragojević, Barčot and Surjan. |
| − | + | Old Vela Luka Dialect is an off shoot of the language spoken in '''17th-18th century''' town of Blato. Etymology of Vallegrande would translate as large bay. From Latin ''grandis'' means large, big whilst ' valle ' in local dialect means bays. Valle (plural) is most probably of Romance (Latin) Dalmatian origin which was spoken by '''Latin Dalmatians'''. The modern name, Vela Luka is an old Croatian translation of Vallegrande, Vela meaning ''large'' and Luka meaning ''bay'' or even port. Within the Liber Legum Statutorum Curzola (Statute of Korčula Town) the written version from 1427, Vela Luka the bay is mention also as "''vela Luca''". With this record we have Croatian-Slavic language influences in the first half of 15th century. The first written Liber Legum Statutorum Curzola was by the Dalmatian Latins and possibly the new Slavic nobility in 1214. | |
| − | Very important to note there is a strong element of Italian Venetian within | + | Very important to note there is a strong element of Italian Venetian within Old Vela Luka Dialect. By the time of 15th and 16th century the majority of the population of the island of Korčula (more in the west end) spoke Old Croatian with a small remnants of the Romance Dalmatian language and with heavy influences of Italian Venetian (''lingua franca'' of that era). During the rule of the Republic of Venice (from 1420 to 1797) saw the disappearance of Romance (Latin) Dalmatian. |
| − | It also has to be taken into account that some parts of the population were bilingual (''or'' even | + | It also has to be taken into account that some parts of the population were bilingual (''or'' even multilingual). |
| − | One could easily say that now the | + | One could easily say that now the 'Old Vela Luka Dialect' (Staro Luški govor) is slowly becoming extinct. Successive Yugoslavian governments, be it the Communist Yugoslavian regime (1945-91) or the earlier Kingdom of Yugoslavia, pushed a Pan-Slavic and Croatian Nationalistic political rule. One of their policies in Dalmatia was Slavicisation of the culture, language and history. Before Yugoslavia came into being the policy was first started to be implemented by Austro-Hungarian Empire, so the original '''Mr Gabrielli''' became Gabrijeliċ. It takes only one generation to change a language, two generations for it too cease to exist. Today's dialect in Vela Luka (Luški Govor, English: Old Vela Luka Speak) is different and has incorporated much of the standardised modern Croatian language (Croatian Literary Standard). |
'''Note''': From the late 19th century onwards the old [[Dalmatian Italians#The Cultural and Historical Venetian Presence in Dalmatia |Dalmatian]] culture has been all but disappearing from the region. | '''Note''': From the late 19th century onwards the old [[Dalmatian Italians#The Cultural and Historical Venetian Presence in Dalmatia |Dalmatian]] culture has been all but disappearing from the region. | ||
| − | The last Italian-language government school was abolished in Korčula on the 13th of September 1876.<ref>[http://books.google.com.au/books?id=kMXURN7sxh4C&pg=PA83&lpg=PA83&dq=The+Italians+of+Dalmatia+Curzola+school&source=bl&ots=Sx1bUxdn1A&sig=YCATl36eEUduI42Azs0GVUeepBo&hl=en#v=onepage&q=The%20Italians%20of%20Dalmatia%20Curzola%20school&f=false The Italians of Dalmatia] by Luciano Monzali (p83)</ref><ref>'''Editor's Note''': The island of Korcula was part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire (1815 to 1918). It was | + | The last Italian-language government school was abolished in Korčula on the 13th of September 1876.<ref>[http://books.google.com.au/books?id=kMXURN7sxh4C&pg=PA83&lpg=PA83&dq=The+Italians+of+Dalmatia+Curzola+school&source=bl&ots=Sx1bUxdn1A&sig=YCATl36eEUduI42Azs0GVUeepBo&hl=en#v=onepage&q=The%20Italians%20of%20Dalmatia%20Curzola%20school&f=false The Italians of Dalmatia] by Luciano Monzali (p83)</ref><ref>'''Editor's Note''': The island of Korcula was part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire (1815 to 1918). It was within the Kingdom of Dalmatia (Konigreich Dalmatien). In the neighbouring '''Kingdom of Croatia ''' (Königreich Kroatien) a [[Croatia|Croatian]] nationalistic movement was established and alongside that, within the Balkan region a Pan-Slavic movement was growing (the beginnings of the ill fated Yugoslavia). These political on goings started to be felt in the Kingdom of Dalmatia. The [[Austria|Austrians]] in the late 1850s started to introduce (a process of [[Croatisation]]) within the Kingdom of Dalmatia a standardised Croatian language sometimes referred to as Illyrian (Illirski). It then replaced Italian altogether. In effect the government undertook culture genocide. For centuries the Italian language was the official language of the Dalmatian establishment. It was also the spoken language in white-collar, civil service and merchant families. Privately Italian schools were still being run in the Kingdom of Dalmatia, i.e the city of Zadar. </ref> |
* Information below taken from Beginnings of Formal Education - Vela Luka: | * Information below taken from Beginnings of Formal Education - Vela Luka: | ||
{{quote| | {{quote| | ||
| Line 348: | Line 357: | ||
== Names of Bays, Fields and Parts of the Town== | == Names of Bays, Fields and Parts of the Town== | ||
| + | * Bad (part of Vela Luka) meaning banda - side - strana (In Venetian it means side & flank) | ||
| + | *'Kale' means ''road'' in Romance language Dalmatian: ''Cale'', (Latin: ''callis'' or path, pathway, sideway, lane, forest pastures, footpath) | ||
* Guvno (part of Vela Luka) | * Guvno (part of Vela Luka) | ||
* Bobovišċa (once not part of Vela Luka but now is) | * Bobovišċa (once not part of Vela Luka but now is) | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* Vranac | * Vranac | ||
| − | * Gradina (a small bay) | + | * Gradina (a small bay, west of Vela Luka) |
* Bradat (a field near Vela Luka) | * Bradat (a field near Vela Luka) | ||
| Line 359: | Line 368: | ||
* [[Korcula Dialect|Korcula Dialect]] | * [[Korcula Dialect|Korcula Dialect]] | ||
* [[Directory:Korcula History 2 |Korcula History, Romans & Venice]] | * [[Directory:Korcula History 2 |Korcula History, Romans & Venice]] | ||
| − | * [[ | + | * [[Dalmatian Italians]] |
| + | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 372: | Line 382: | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | ---- | ||
[[File:85px-Coat of arms of Croatia.svg.png||thumb|left|250px|Coat of arms of Croatia (Hrvatska)]] | [[File:85px-Coat of arms of Croatia.svg.png||thumb|left|250px|Coat of arms of Croatia (Hrvatska)]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:17, 13 December 2024
Old Vela Luka Speak in Croatian, Staro Luški govor [1] (or alternatively it could be called Vallegrande Speak) is an old Korcula Dialect from the small town of Vela Luka. The town is on the west end of the island of Korčula.[2] The island of Korčula lies just off the Dalmatian coast in Croatia.[3] The language base of this Korčula Dialect is Croatian Chakavian [4] (it is also intermixed with Old Western Shtokavian[5]). It has very strong elements of Italian Venetian and it also has small remnants of the extinct Romance (Latin) language, Dalmatian [6][7][8]. The Dalmatian remnants within the dialect have been sometimes referred to as Corzulot. The local dialect is sometimes referred to as 'Naški' [9] (the š is pronounced sh).
The island was from 1420 to 1797 part of the Republic of Venice (the French Empire dissolved the Republic [10] in 1797). The Old-Slavic term was Krkar. According to Antun (Antonio) Rosanovic written in his Defence of Korcula in 1571 the Greeks named it Corcyra Melena.[11]
One of Korčula's older names was Curzola. Vela Luka in the past was called Vallegrande (Latin: vallem maximam).

Chronology-Korcula Island Languages
- Illyrian (Delmatae)
- Greek
- Latin (Romans)
- Romance Dalmatian (Vulgar Latin)
- Croatian (Slavic Chakavian)
- Venetian (Romance language)
- Old West Shtokavian - Slavic
- Italian (standardise language arrived, besides Latin)
- Croato-Serbian (Slavic standardise language[12] also known as Serbo-Croatian, based on Neo Štokavian[13])
Modern times
- Croatian (Croatian Literary Standard, standardise language)
Words from the Old Vela Luka Dialect - Staro Luški
Old Vela Luka Dialect - English - Croatian
Template:Col-break- A boje da ni - yes of course it is - Dakako da jeste
- adio - goodbye - doviđenja (addio: meaning in Italian goodbye)
- adojat - to please (aldojat: meaning in Romance Dalmatian to feel at home, to be settled)
- afitat - rent (Venetian Italian: afìt)
- aimemeni or aime meni - poor me or oh dear, dear me
- alavia - done properly or it's Ok!, just right - u redu (Romance Dalmatian just right)
- apoteka - pharmacy (Venetian: apoteca, Greek: Apotheke)
- arbol - ship's mast
- aria - air - zdrak (Venetian: aria)
- arma - armed (Venetian: arma)
- ašeta - a type of tool
- avižat [14] - to arrive - došao
- bala - dance - plesati (Venetian: baleto)
- balanca - balance, weighing scale
- baleta - bullet - metak (Venetian: bal)
- banda - side - strana (In Venetian it means side & flank)
- balun - football (Venetian: balón)
- banak - bench (Venetian: banca) [15]
- baraka - shed or shack (Venetian: baràca)
- barba - uncle - stric (Venetian: barba)
- bareta - cap, hat (Venetian: baret)
- barilo - barrel (Venetian: barìla)
- barka - type of local boat (Venetian: bàrca)
- bašje - lower (Romance Dalmatian: bas de)
- bat - a type of hammer (Venetian: batu meaning to strike)
- bevanda - wine with water - vino sa vodom (Venetian: bevànda "watery wine")
- beštija - animal - životinja (Latin: bestia also beast)
- beštimat - swear (Venetian: bestiemàr)
- bičve - socks - čarape
- bićerin - small glass (Venetian: bicér "glass")
- bilo - white - bjelo
- bira - beer - pivo (Venetian: bira)
- bluza - female shirt - ženska košulja
- Brigela - local nickname (Venetian: brighela joker)
- brokva - nail
- bobon - lolly
- boca - bottle - flaša (Venetian: boca)
- bome - of course - naravno (Romance Dalmatian: bome)
- bonaca - the sea is dead calm (Venetian: bonàça)
- botilja - bottle (Romance Dalmatian: botaila)
- botun - button (Romance Dalmatian: botaun)
- bravo - well done
- buka - noisy - glasan (Romance Dalmatian: buka)
- bukva - herring
- bura - local wind (Venetian: bora)
- burlsa - bag
- butiga - shop
- buža - hole - rupa (Venetian: bus or buxa)
- cilo - wine without water - vino bez vode
- Cilo doba sam bi tu - I was there all along - Tu sam bio neprestano
- cima - rope’s end (also called bitter end); rope put overboard; edge, end or tip of something. Origin: The earliest record of the term is the Italian - cima, at the beginning of the 17th century. [16]
- cukar - sugar - šečer (Venetian: sucaro)
- čakule - gossip (č is ch)
- čagalj - jackal
- čejad - people - ljudi
- ćìkara - small cup - šalica (Venetian: chicara)
- čorav - blind (Venetian: ciòro "blind person")
- damižana - a netted bottle
- daska - small plank
- daž - rain - kiša
- Defora in old Venetian means "from the outside".
- denti - teeth - zubi (Romance Dalmatian)
- dobota - nearly - (Venetian: dedoto or doboto)
- dreto - straight (Romance Dalmatian: drat)
- di - where - gdje
- dite - child - djete
- Di greš?- Where are you going?
- Di si? Where are you?
- Esi ija? or Esi izja? - Did you eat?
- ižejat - to work out or improvise
- ipo - half
- iza - after or above
- izija - ate
- izvrtit - to undo a screw
- faca - face - lice (Venetian: faca)
- fabrika - factory - tvornica (Latin: fabrica- manufacture or to craft, trade, art, trick, device)
- fabrikat - to trick
- falso - fake (Venetian: falso "liar")
- farmacia - pharmacy - Apoteka (Romance Dalmatian)
- fatiga - work - radi
- febra - fever
- feral - a gas or petroleum lamp for attracting fish (night fishing). Also in Venetian feral means "lamp".
- fermai - stop - stani (Italian: fermare verb 'stop')
- feta - slice (Venetian: feta)
- feca - wine sludge
- figura - figure (Venetian: figura)
- fjaka - When one feels sleepy on a lazy summer day afternoon.
- forma - shape (Venetian: forma)
- fraja - to go out and have a good time (Venetian: fraja-happy company or happy bunch)
- fratar - brother - brat (Romance Dalmatian)
- frigati - to fry (Romance Dalmatian: fregur)
- frižul - a spot to have a chat, on a stone bench [17] (Romance Dalmatian: faul or faular, meaning to speak)
- forca - power (apply with strength)
- fortuna - strong wind
- fratar - priest (Latin: frater meaning brother)
- fuga - gap (Latin: flight, escape)
- fumar - chimney (Venetian: fuma meaning smoke)
- fumati - smoking - pušiti
- furešti - foreigner - stranac
- gače - pants
- gira - a fish from Croatia.
- gradele - grill - roštilj; sprava za pečenje na žaru (Venetian:graèla)
- gre - going
- grintav - they are in a bad mood
- griža - a form of very hard stone
- gundula - type of boat
- gusti - enjoyment (Venetian: gusto-pleasurable)
- gusto - thick
- gustrina - underground rainwater reservoir
- guzica - bottom
- hoča or homoča (more group related) - lets go
- kacavida - screwdriver
- kadena - chain (Romance Dalmatian:kataina)
- kajić - type of local boat
- kajiš - belt
- Kalafat - means masters (shipyard workers) who filled the fissures between boards on a wooden boat.
- kamara - bedroom - soba (Latin: camera-vault, vaulted room)
- kantat - to sing - pjevati (Latin: canto)
- kapelīn - small female hat - maleni ženski šešir (Venetian: capelìn or piccolo cappello)
- kapula - onion - luk (Romance Dalmatian: kapula)
- karoca - small carriage (Venetian: carosa)
- kašeta - small wooden box
- kašun - large box
- katrida - chair - stolica (Romance Dalmatian: katraida)
- katun - corner (Latin: cantus)
- klapa - an a cappella form of music [18] (Venetian: clapa "singing crowd")
- keleh - the floor
- kolbuk - hat
- koltrine - curtains (Venetian: coltrina)
- konoba - cellar
- kontra - against - protiv (Latin: contra)
- korač - hammer
- koraj - full of himself - (Venetian: coràjo means courage)
- kormilo - rudder
- krepa - died - umro (Venetian: crepar meaning die also means crack)
- kuntra - bump into
- kušin - pillow - uzglavlje or jastuk (Venetian: cussin)
- kužina - kitchen - kuhinja (Venetian: cuxìna)
- kužin - cousin - rođak (Venetian: cuxìn)
- lacun - bed sheets (Romance Dalmatian: lenzul)
- lamin - sheetmetal bucket
- lanterna - lighthouse - svjetionik (Venetian: lanterna)
- lapis - pencil - olovka (Venetian: apis)
- lata - tin (Venetian: lata)
- lavadin - washbasin (Venetian: lavandin)
- laz - a small part of a agriculturally worked land.
- leć - sleep - spavati (Romance Dalmatian: lat meaning bed)
- lešada - a type of fish soup (boiled)/ Lesada in Venetian means boil.
- leut - type of local boat
- levant - local wind
- libro - book - knjiga
- licenca - licence - dozvola (Venetian: icenca)
- lipo - nice or beautiful - ljepo
- očetavat - to unhook, sort out
- mahnit - crazy, unstable, nuts
- maistral - local coastal wind
- makina - machine
- makina od pranja- washing machine
- Malandrin - Local nickname. In Venetian it means: dishonest or crook
- mapa - map (Venetian: mapa)
- Maragun - wood worker (Venetian: Marangòn)
- maza - to be spoiled, the spoiled one (Venetian: maza)
- Ma or mat - mother - majka
- mećat - to throw
- meja - a stone wall in the field (drystone fence, Ita: muretto a secco)
- mezo - in between (Venetian: mèzo "half")
- Mi povidamo na našu or Mi pripovidamo na našu- Mi pričamo naš jezik (in neoshtokavian)
- mir/ wall - Dalmatian: mir (Croatian: zid)
- mlinko - milk
- mola - let go
- motika - local agricultural tool
- mudante - underwear (Venetian: mudande)
- munita - change money (Romance Dalmatian: monaita)
- munka - flour - brašno
- noštromo - boatswain
- ofinditi - to insult
- parlaš - talking - govoriti (Venetian: he speaks or Romance Dalmatian: palaura meaning word)
- parti - leaving
- pamidora - tomato (Italian: pamidore)
- pandur - policemen - policija (Venetian: panduro)
- panja - bread - kruh
- papit - this word is used when feeding a child - jedi djete (Venetian: papa-means baby food)
- patakuni - small change - mali/sitni novac (Romance Dalmatian)
- patalone - pants
- perun - fork (Venetian: pirón from Greek: pirouni)
- piat or pijat - plate
- pikolo - small, little (Venetian: picolo)
- Pelišac - Pelješac (other names used: Pelisac, Stonski Rat, Puncta Stagni, Ponta di Stagno and Sabioncello)
- pirula - pill - tableta (Venetian: pirola)
- pistun - piston (Venetian: piston)
- priša - in a hurry - (Venetian: presá - meaning hast)
- prusura/frying pan - Dalmatian: prasura [19]
- pitura - paint (Venetian: pitura-painting)
- piz - weight (Latin origin, Venetian: pexa meaning weighing)
- poć na ribe - going fishing - ići na ribanje
- pod - upper floor (Venetian: podolo - meaning balcony)
- popričat - lets discuss
- postelja - bed - krevet
- postoli - shoes - cipele
- pripovidat - to tell a story
- probi - penetrate
- provaj - give it a try, to test it out (Venetian: pròva - meaning test)
- prskat - mini shower
- prat- wash
- pule - baby donkey
- punte - points
- punistra - window (Latin: fenestra)
- puntižel - plank, board
- reful - small strong wind a gust
- regeta - light sheet metal
- rič - word
- ritko - not often
- roba - clothes - odjeća
- rotunda - circular dry stone building - vrtujak
- sak - bag (Venetian: saco)
- senjat - to mark
- setemana - week - tijedan (Venetian: setemana)
- skala - stairs (Venetian: scala, scalinada)
- skula - school - škola
- skuža - understood, work it out
- snig - snow - snjeg
- spim - I'm sleeping
- spirit - ghost - duh
- spiza - food - hrana
- soldi - money - novac (Latin: solidus)
- soto - underneath - ispod (Venetian: sot or soto)
- sritan - happy or lucky - sretan
- stezi - tighten
- šegac - saw
- šestan - attractive or good looking (Venetian:sesto-grace, well mannered)
- šija - reverse - natrag
- šiloko - local wind (Venetian: siròco)
- škina - back (spine) - leđa
- škoj - island - otok
- škver - shipyard - brodgradilište
- špina - tap (Venetian: spina)
- špirit - ghost - duh (Venetian: spirito. In local Vallegrande Speak it can mean strong alcohol)
- šporko - dirty (Venetian: spórco)
- štivo - book - Knjiga
- štrada - street - ulica (Italian: strada)
- šufit - attic or loft (Venetian: sofìta)
- šugaman - beach towel
- šujat - to trick
- takat - to roll olives to remove leaves
- tanac - dance - ples
- tastamenat - confession or a will
- tata - father - otac (Latin Romance language Dalmatian: Tuota)
- tavajola - tablecloth (Venetian: toaja)
- teće - leaking
- tereina or teća - metal bowl (Venetian: tereina)
- terpeza - table - stol
- tira - pull
- timul - driving wheel, ships or boats wheel, rudder (Venetian: timon)
- torta - a type of cake (Romance language Dalmatian: Turta)
- tovar - donkey - magarac
- traversa - apron - pregača (Venetian: traversa)
- tudin - small round steel bar
- ura - hour - jedan sat
- umideca - damp - vlaga (Venetian: umidic)
- vagun - ten tones
- vala - bay (vale - bays)
- vapor - ferry - trajekt (Venetian: Bapor meaning steamship)
- vara vamo - move on or move over there, these are commands for local donkeys when on the move
- vedro - clear sky (Romance Dalmatian: vedar - to see)
- vesta - dress - ženska haljina (Venetian: garment, vestir: dress)
- vela - big - veliko
- vida - screw
- Vi ga niste vidili - You did not see him.
- vlasi - hair - kosa
- volja - desire, wanting too, mood - želja (Venetian: wish, desire, Can be used i.e. Nije mi volja. Meaning - I'm not in the mood or I'm not feeling too good.
- zamantan - crazy - lud
- zamuti - to stir
- Za fatigu je just - For work he is perfect - Za posao je izvrstan
- Zapiha sam se - I've lost my breath - izgubio sam zdrak
- zrcalo - mirror - ogledalo
- zeje - local dish
- žeja - thirsty (the ž is pronounced zh)
- želizo - axe - sjekira
- žmul - glass - čaša
Additional History
Trying to re-tell the history of this part of the world (old Dalmatia part of Croatia) is fraught with problems. The Yugoslav Communist party was the main driving force in all social matters within the former Yugoslavia. It created historic falsehoods to promote its own aggressive political authoritarian agenda.
We can definitely confirm that from the 13th century onwards there were two ethnic communities living on the island in the middle ages [20][21][22], one being descendants of the Roman Empire and the other being of Slavic descent.
Two languages became the norm on the island, firstly the Romance Latin language called Dalmatian, then we have the arrival of old Slavic Croatian Chakavian language. With time these languages started to overlap with a form of bilingualism being created (with the written language being Latin). The fact that Slavs from the old neighbouring Kingdom of Croatia also spoke old Slavic Chakavian could indicate that this group of Slavs came from the same or similar tribal group.
When the Serbian forces were annihilated in the Battle of Kosovo by the Ottoman Empire (Ottoman Turkish: دولت عليه عثماني) in 1389 a large group of peoples started a exodus westward (Byzantine's Constantinople fell to the Ottoman Empire - Turks in 1453). Venetian Dalmatia (Dalmazia Veneta) started to acquire new people in its region (i.e., Eastern Croatians - Hercegovci, Montenegrins, Albanians, Serbs & others) and add to the fact that the Black Plague [23][24][25] depleted the island's population the Venetian authorities saw a need to bring new families to the island of Korčula. Amongst these were Western Shtokavian Slavic speakers. With these new added migrations the Slavic speakers became a strong majority. This applies more to west end of the island, with the village of Račišće being the exception (the village is in the eastern part of the island).
If the translation of the Defence of Korčula from Ottoman Turkish Attack in 1571 (Corcyrae Melenae Opus - Antonii Rosanei), originally written by Antun (Antonio) Rozanovic is untainted, we can see that the majority of the defenders of the island were by 1571 of Slavic decent. If we use this as a reference, then from the mid 16th century onwards the majority of Korčula's population was indeed of Slavic origins.
Old Vela Luka Dialect Evolved Late 18th Century
Vela Luka's first beginnings as a town, are from the late 17th century (late 1600s). It started with the population of the neighbouring Blato [26] setting up a town with a port in the large bay of Vela Luka (Vallegrande or Latin: vallem maximam). Zvonko Maričić (Maricich) states in the late 1500s there where already five buildings in the bay (one being a church). The buildings belong to Ismaelli, Gabrielli, Canavelli[27] and Kolovic.
Then around the 1690s [28] there were additional twelve households (written in modern Croatian): Draginić, Tulić, Nalošić, Kostričić, Cetinić, Mirošević, Žuvela, Prižmić, Marinović, Dragojević, Barčot and Surjan.
Old Vela Luka Dialect is an off shoot of the language spoken in 17th-18th century town of Blato. Etymology of Vallegrande would translate as large bay. From Latin grandis means large, big whilst ' valle ' in local dialect means bays. Valle (plural) is most probably of Romance (Latin) Dalmatian origin which was spoken by Latin Dalmatians. The modern name, Vela Luka is an old Croatian translation of Vallegrande, Vela meaning large and Luka meaning bay or even port. Within the Liber Legum Statutorum Curzola (Statute of Korčula Town) the written version from 1427, Vela Luka the bay is mention also as "vela Luca". With this record we have Croatian-Slavic language influences in the first half of 15th century. The first written Liber Legum Statutorum Curzola was by the Dalmatian Latins and possibly the new Slavic nobility in 1214.
Very important to note there is a strong element of Italian Venetian within Old Vela Luka Dialect. By the time of 15th and 16th century the majority of the population of the island of Korčula (more in the west end) spoke Old Croatian with a small remnants of the Romance Dalmatian language and with heavy influences of Italian Venetian (lingua franca of that era). During the rule of the Republic of Venice (from 1420 to 1797) saw the disappearance of Romance (Latin) Dalmatian.
It also has to be taken into account that some parts of the population were bilingual (or even multilingual).
One could easily say that now the 'Old Vela Luka Dialect' (Staro Luški govor) is slowly becoming extinct. Successive Yugoslavian governments, be it the Communist Yugoslavian regime (1945-91) or the earlier Kingdom of Yugoslavia, pushed a Pan-Slavic and Croatian Nationalistic political rule. One of their policies in Dalmatia was Slavicisation of the culture, language and history. Before Yugoslavia came into being the policy was first started to be implemented by Austro-Hungarian Empire, so the original Mr Gabrielli became Gabrijeliċ. It takes only one generation to change a language, two generations for it too cease to exist. Today's dialect in Vela Luka (Luški Govor, English: Old Vela Luka Speak) is different and has incorporated much of the standardised modern Croatian language (Croatian Literary Standard).
Note: From the late 19th century onwards the old Dalmatian culture has been all but disappearing from the region. The last Italian-language government school was abolished in Korčula on the 13th of September 1876.[29][30]
- Information below taken from Beginnings of Formal Education - Vela Luka:
Names of Bays, Fields and Parts of the Town
- Bad (part of Vela Luka) meaning banda - side - strana (In Venetian it means side & flank)
- 'Kale' means road in Romance language Dalmatian: Cale, (Latin: callis or path, pathway, sideway, lane, forest pastures, footpath)
- Guvno (part of Vela Luka)
- Bobovišċa (once not part of Vela Luka but now is)
- Vranac
- Gradina (a small bay, west of Vela Luka)
- Bradat (a field near Vela Luka)
See also
External Links
Notes & References
- ^ Tako su stari govorili. Translated: That's how the old folk use to speak.
- ^ The č is pronounced ch.
- ^ John Everett-Healu. "Dalmatia." Concise Dictionary of World Place-Names. Oxford University Press. 2005. Encyclopedia.com
- ^ Editors note: Slavic tribes invaded the region of Roman Dalmatia in the early Middle Ages. Prior to the arrival of the Slavs, Roman Dalmatia was mainly inhabited by a Roman Latin-Illyrian population. Recent DNA studies have stated that more than three quarters of today's Croatian men are the descendants of Europeans who inhabited Europe 13 000-20 000 years ago (prior to the arrival of the Slavs). The first primary source (factual-that its authenticity isn't disputed) to mention the Croatian (Hrvat) identity in the Balkans was Duke Branimir (Latin: "Branimiro comite dux cruatorum cogitavit" c. 880 AD). Branimir was a Slav from Dalmatia.
- ^ The Land of 1000 Islands by Igor Rudan
- "However, the clashes between the Ottoman Empire and Venetian Republic produced extensive migrations from the mainland areas, especially from today's Bosnia and Herzegovina, to the eastern parts of the islands of Brač, Hvar, Korčula, and Pag [Dalmazia Veneta]. The newcomers brought their gene pool and a variety of cultural specificities, including the Shtokavian dialect of the Croatian language to the predominantly “Chakavian” area. The most extensive migrations to these islands occurred during the Cypriote (1571-1573), Candian (1645-1669), and Morean wars (1684-1699)."
- ^ PRILOG PROUČAVANJU LEKSIČKIH RAZLIKA IZMEĐU GOVORA BLATA I VELE LUKE (I) by Petar Milat Panža (Eng: Contribution to the Study of Lexical Differences Between the Speech of Blato and Vela Luka): ..... a famous Croatian linguist finally asserted that there is no Slavic studies without Roman studies! He admitted that it is not possible to study the Croatian language with its three dialects - Štokavian, Kajkavian and Chakavian - without studying Romance influences, especially on our Chakavian languages. By the term Romanic influences, we understand remnants from Latin through Dalmatian (Old Dalmatian, Dalmatian-Romance), then remnants from Venetian and all other Italian dialects, and finally the influences of the standard Italian language. Another group worthy of research is the lexicon of Slavic origin, which appears in the speech of Vela Luka, but is not present in the speech of Blato.
- ^ Encyclopedia Britannica
- ^ Dalmatian Language (Wikipedia)
- ^ Note: Naški means 'ours' thus meaning "our language" in Croatian.
- ^ Note: In old Venetian 'Repùblega Vèneta' also know as La Serenissima
- ^ Greek: Kórkyra Melaena or Κόρκυρα Μέλαινα, and Corcyra Nigra (Latin)
- ^ Standardise Croatian arrived in the late 1850s. The Standardise language was referred to as Illyrian (Illirski). Ref from Osnovna Škola "Vela Luka" Vela Luka Zbornik-150 Godina Školstva u Velaoj Luci, p.50 written in Croatian
- ^ Language and Identity in the Balkans: Serbo-Croatian and Its Disintegration ... By Robert D. Greenberg
- ^ The ž is is pronounced zh.
- ^ Venetian-English English-Venetian: When in Venice Do as the Venetians by Lodovico Pizzati (p19)
- ^ Lingua Franca in the Dalmatian Fishing and Nautical Terminology by J.Božanić
- ^ 'Da Se Ne Zaboravi: Rječnik, Stare Priče, Običaji i Zanati u Blatu na Otoku Korčuli' by Žanetić Pudarić, Blato 2009 (Eng: Let's Not Forget: Dictionary, Old Stories, Customs and Trades in Blato on the Island of Korcula) . In Croatian, meaning taken from the book: "ižul - niska kamena klupa uz kuću koja služi za odmaranje, ćakulu, za prtit stoku, itd (a low stone bench next to the house that is used for resting, discussions ....., etc."
- ^ The traditional Klapa was composed of around half of dozen male singers (in recent times there are female Klape groups). Klapa singing dates back centuries. The arrival of the Slavic-Croatians to Dalmatia and their subsequent settlement in the area, began the process of the cultural mixing of Slavic culture with that of the traditions of the Roman population of Dalmatia. This process was most evident in the coastal and island regions of Dalmatia. In the 19th century a standard form of Klapa singing emerged. Church music heavily influences the arrangements. The modern Klapa style was established in the 1960s.
- ^ Nikola Vuletić - Croatian in the Mediterranean Context: Language Contacts in the Early Modern Croatian Lexicography
- ^ When Ethnicity Did not Matter in the Balkans: by John Van Antwerp Fine. (p103)
- ^ Smiciklas, CD V, (p237)
- ^ N. Klaic, Povijest Hrvata u Razvijenom, (p83)
- ^ Korcula was devastated by the plague in 1529 and 1558.""Korcula." Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encyclopædia Britannica, 2011. Tue. 8 Mar. 2011." (2011). Retrieved on 2011-03-8.
- Encyclopædia Britannica: " A plague devastated the town in 1529, depleting the population. The burned houses of infected persons, called kućišta..."
- ^ The Shores of the Adriatic (Illustrated Edition) by F Hamilton Jackson (p239)
- ^ Plague Epidemic on the Island of Korcula 2007 by Nikola Bačić 2007: " 13. EPIDEMIC 1617. It swept all of Dalmatia, but left the most severe consequences on the island of Korčula. It appeared first with the sailors of the Venetian ship (as N. Ostojić describes) who wintered in Korčula that year. Suburban homes had to be emptied to turn into dwellings for diseased sailors. The contagion soon spread to citizens and within a few months more than half of the population had died. A particularly devastating disease was, according to the data, for wealthier residents, so many entire noble families who had a reputation for their homeland were extinct."
- ^ In Croatian blato means mud it also has been said the word is related to water referring to the once lake in neighbouring field
- ^ In re-written modern Croatian: Kanavelić
- ^ Vela Luka od 1490 do 1834 by Zvonko Maričić (p207)
- ^ The Italians of Dalmatia by Luciano Monzali (p83)
- ^ Editor's Note: The island of Korcula was part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire (1815 to 1918). It was within the Kingdom of Dalmatia (Konigreich Dalmatien). In the neighbouring Kingdom of Croatia (Königreich Kroatien) a Croatian nationalistic movement was established and alongside that, within the Balkan region a Pan-Slavic movement was growing (the beginnings of the ill fated Yugoslavia). These political on goings started to be felt in the Kingdom of Dalmatia. The Austrians in the late 1850s started to introduce (a process of Croatisation) within the Kingdom of Dalmatia a standardised Croatian language sometimes referred to as Illyrian (Illirski). It then replaced Italian altogether. In effect the government undertook culture genocide. For centuries the Italian language was the official language of the Dalmatian establishment. It was also the spoken language in white-collar, civil service and merchant families. Privately Italian schools were still being run in the Kingdom of Dalmatia, i.e the city of Zadar.
- ^ The Early Beginnings of Formal Education - Vela Luka (beginnings of literacy and Lower Primary School 1857 – 1870) (p.12 written in Croatian, part of Vela Luka Zbornik-150 Godina Školstva u Velaoj Luci )
Korcula Korčulanski Directory:Korcula History Korcula History Corzulot Korzulot Croatian dialect Dalmatian Venetian Latin Klapa Vela Luka Blato Croatia Dalmatia Korcula Korčula Dalmatia Dalmatian Language Guvno