Difference between revisions of "Dalmatian Italians"
(Editing Dalmatian Italians) |
|||
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
[[File:Perasto (1900).jpg|thumb|right|325px| Postcard showing the Venetian architecture of Perast in 1900]] | [[File:Perasto (1900).jpg|thumb|right|325px| Postcard showing the Venetian architecture of Perast in 1900]] | ||
=== Perast in Coastal Montenegro === | === Perast in Coastal Montenegro === | ||
| − | An example of the Venetian cultural and historical presence can be seen in the small town of Perast (Perasto) in coastal Montenegro. Perast under the Republic of Venice (Albania Veneta), had four active shipyards, a fleet of around one hundred ships, and 1,643 residents. Some of the buildings are ornate baroque palaces which was typical Venetian architecture. The town kept the war-flag of the Venetian | + | An example of the Venetian cultural and historical presence can be seen in the small town of Perast (Perasto) in coastal Montenegro. Perast under the Republic of Venice (Albania Veneta), had four active shipyards, a fleet of around one hundred ships, and 1,643 residents. Some of the buildings are ornate baroque palaces which was typical Venetian architecture. The town kept the war-flag of the Venetian Navys, called ''"La fedelissma Gonfaloniera"''. |
The sailors of Perast were involved in the last battle of the Venetian navy, fought in Venice in 1797. At the fall of the "Serenissima" (1797) Perast was the last city of the Republic to lower the Venetian flag. On 12 May 1797, the Republic of Venice ended, but a few places in the Albania Veneta for several months still continued to remain loyal to the Venetian Republic. On 22 August 1797 the Count Giuseppe Viscovich, Captain of Perast, lowered the Venetian war-flag of the Lion of Saint Mark pronouncing the farewell words in front of the crying people of the city and buried the "Gonfalon of Venice" under the altar of the main church of Perast. | The sailors of Perast were involved in the last battle of the Venetian navy, fought in Venice in 1797. At the fall of the "Serenissima" (1797) Perast was the last city of the Republic to lower the Venetian flag. On 12 May 1797, the Republic of Venice ended, but a few places in the Albania Veneta for several months still continued to remain loyal to the Venetian Republic. On 22 August 1797 the Count Giuseppe Viscovich, Captain of Perast, lowered the Venetian war-flag of the Lion of Saint Mark pronouncing the farewell words in front of the crying people of the city and buried the "Gonfalon of Venice" under the altar of the main church of Perast. | ||
Revision as of 00:21, 9 May 2011
The region of the former Yugoslavia (Western Balkans) has problems when interpreting its multicultural, multiethnic history and societies. This most certainly applies to the history of Dalmatian Italians, the former Republic of Ragusa and other regions. The statement below comes from a book called Dalmatia (History, Culture, Art Heritage) written by Antun Travirka:
| “ | By the 14th century the city had become wholly Croatian [1] | ” |
The book itself is primarily for the tourist market and is easily available in several languages. This quote is on page 137 and it’s referring to the Republic of Ragusa. The old Republic of Ragusa (with it's famous city Dubrovnik) [2][3][4] is now within the borders of the modern Croatia. This monolithic description is an outright lie and it’s a form of cultural genocide (the crucial word is wholly). Additionally the book did not even use the term Republic of Ragusa (the closest that it got to this was RESPUBLICA RAGUSINA on page 141),[5] which was used for more than a millennium. The Republic was set up by Latin/Illyrian families and was a nation in its own right. It was also made up of many ethnic nationalities.[6][7][8][9] As a Maritime nation it traded all over the Mediterranean and even had trade with the Americas. Additionally it was in competition with Venice, the most powerful and influential maritime nation during that era.
- Statement made by the contemporary historian John Van Antwerp Fine:
| “ | This is not surprising since the “Ragusans” identified themselves as Ragusans and not as Croats.[10] | ” |
The former Communist Yugoslavia (which Croatia was part of) played a major role during the Cold War era in depicting this style of historical documentation (Dalmatia - History, Culture, Art Heritage) of the region’s past. Yugoslav Communist history is now dogma in Croatia. This also would apply to the history of the Dalmatian Italians. Many of today’s Croatians live with this dogma as their reality even though the Berlin Wall fell in 1989. The Communist Party of Yugoslavia had a profound effect on the region.[11] So much so that it has created today’s political and cultural scene.
- Statement made by the contemporary historian Danijel Dzino:
| “ | Medieval studies in Croatia and in most of the former Yugoslav space were firmly rooted in political history and suffered from isolationism and lack of interest in foreign scholarship. In the communist era, especially after the 1960s, Marxist ideology and national and Yugoslav political-ideological frameworks strongly impacted on the research into medieval history in Croatia [12] | ” |
- Statements made by the contemporary historian John Van Antwerp Fine (Professor Emeritus of History at the University of Michigan):
| “ | Such substitutions of “Croat” for” Slav,” however, mislead the reader into believing something the sources do not tell...[13]
|
” |
Note: Communist Yugoslavia executed Historian - Kerubin Segvic. He was executed mainly for proposing a different historic model of how Croats came to the western Balkans in the middle ages than that of the Yugoslav government's state policies. [15]
This article is a work in progress. Sections of the article is transferred from Wikipedia.
|
Dalmatian Italians
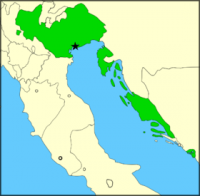
Dalmatian Italians are a Italian national minority in the region of Dalmatia (today part of Croatia).
When Austria occupied Dalmatia the Italian (Venetian speaking) population made up, (according to the Italian linguist Bartoli) nearly one third of Dalmatia in the first half of the 19th century. The 1816 Austro-Hungarian census registered 66 000 Italian speaking people among the 301 000 inhabitants of Dalmatia, or 22% of the total Dalmatian population. After World War II, the Dalmatian Italian population was reduced to 300 in Dalmatia and 500 in Montenegro. [16][17][18]
Today they reside mostly in the city areas of Zadar (Zara), Split (Spalato), Trogir (Trau), and Sibenik (Sebenico) in Croatia, and Kotor (Cattaro), Perast (Perasto), and Budva (Buduain) in Montenegro. In other parts of Croatia, there are estimated to be 20 000 Italians in total, most are located in communities in the Istrian peninsula and the city of Rijeka (Fiume).
Early History
Roman Dalmatia
Roman Dalmatia was fully latinized by 476 AD when the Western Roman Empire disappeared, according to scholar Theodor Mommsen in his book "The Provinces of the Roman Empire". More recent theories have suggested that this would only apply to cities and towns, whilst in the country side, this would not have been the case.
During the Barbarian invasions of the 6th and 7th century, [19] Eurasian Avars allied with certain Slavic tribes [20][21] invaded and plundered Byzantine-Roman Dalmatia. This eventually led to the settlement of different Slavic tribes in the Balkans. Modern scholarly research now puts the time of the invasion of the Slavic tribes in the region to be much later.[22] Archaeological evidence found in the old Roman city of Salon and in particular the artefacts found at the Old Croatian grave sites in Dalmatia (during recent excavations) [23] seems to confirm this. Some historians have placed the arrival of Slavs in larger groups now to be more in the region of the 8th century.
The original Roman population endured within the coastal cities [24] and in the inhospitable Dinaric Alps (these people were later known as "Morlachs" or Vlachs). Many Dalmatian cities retained their Romanic culture and Latin language. Among these were Zadar (Jadera/Zara), Split (Spalatum/Spalato), Dubrovnik (Ragusa) and Trogir (Trau). These areas developed their own Vulgar Latin, the Dalmatian language,[25] a now extinct Romance language.[26] Many coastal cities and towns or the region (politically part of the Byzantine Empire) [27] maintained political, cultural and economic links with the Italian peninsula through the Adriatic sea. Communications with the mainland were difficult because of the Dinaric Alps. Due to the sharp orography [28] of Dalmatia communications between the different Dalmatian cities occurred mainly through sea links. This helped Dalmatian cities to develop a unique Romance culture, despite the mostly Slavicized mainland.
Late Middle Ages and Early Renaissance
From the late Middle Ages onwards certain sections of the population slowly started to merge with the Slavic peoples of Dalmatia. This process was most evident in the coastal and island regions of Dalmatia and in the Republic of Ragusa. The 1667 Dubrovnik earthquake,[29] which destroyed the greater part of Dubrovnik (Ragusa) has been cited as a turning point for the make up of the ethnic population of the Republic. This new Slavic population within the Republic became, with time, Romanised (adopted Latin culture). Within Ragusa's community there were mixed marriages (i.e. Roger Joseph Boscovich).[30]
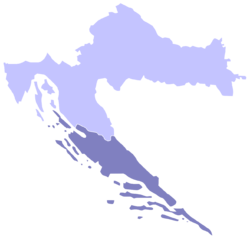
Croatians in Dalmatia, as well as other regions, have language remnants of the extinct Romance Latin language - Dalmatian and additionally there are influences of old Venetian in the local dialects. The Republic of Venice controlled most of Dalmatia from 1420 to 1797. During that period, part of its Slavic population were Romanised.
"Venetian Dalmatia", as it was named by the Venitians, enjoyed periods of economic prosperity with the development of arts and culture. Dalmatia was greatly influenced by the Italian Renaissance and many buildings, churches and cathedrals were constructed in those years, from Zadar and Split to Sibenik (Sebenico) and Dubrovnik.
Zadar was the capital of Venetian Dalmatia. During these centuries, the Venetian language became the "lingua franca" of all Dalmatia, assimilating the Dalmatian language of the Romanised Illyrians and influencing partially the coastal Croatian language (Chakavian).
It is also important to mention migrations from the east, as the Ottoman Empire advanced into Europe. Wars with the Ottoman's and other conflicts were all part of Venetian Dalmatia's history as well as internal strife within the province (i.e.Hvar Rebellion). [31] Looking back through its past, Dalmatia presents it self as a region of Europe with a very multicultural and multiethnic history.[32]
The Cultural and Historical Venetian Presence in Dalmatia
The cultural and historical Venetian presence in Dalmatia is related to the northern Italian influences in Dalmatia. The original Roman Dalmatia is now divided between Croatia, Herzegovina and Montenegro. The cultural influence from the Republic of Venice is clearly evident in the urbanisation plans of the main Dalmatian cities. One of the best examples is the one of Split.
In 1880 Antonio Bajamonti (the last Dalmatian Italian Mayor of Split under Austrian rule) developed an urbanisation project of this city centred on the "Riva", a seaside walkway full of palms based on the Italian Riviera models. Even today the Riva (with cafe bars) is used by the locals to stroll in a typical Italian way from the "Palace of Diocletian" towards an old square called locally "Pjaca" (or square in Venetian).
In Dalmatia, religious and public architecture flourished with influences of the Italian Renaissance evident. Important to mention are the Cathedral of St James in Sibenik, the Chapel of Blessed John in Trogir, and Sorgo’s villa in Dubrovnik.
Perast in Coastal Montenegro
An example of the Venetian cultural and historical presence can be seen in the small town of Perast (Perasto) in coastal Montenegro. Perast under the Republic of Venice (Albania Veneta), had four active shipyards, a fleet of around one hundred ships, and 1,643 residents. Some of the buildings are ornate baroque palaces which was typical Venetian architecture. The town kept the war-flag of the Venetian Navys, called "La fedelissma Gonfaloniera".
The sailors of Perast were involved in the last battle of the Venetian navy, fought in Venice in 1797. At the fall of the "Serenissima" (1797) Perast was the last city of the Republic to lower the Venetian flag. On 12 May 1797, the Republic of Venice ended, but a few places in the Albania Veneta for several months still continued to remain loyal to the Venetian Republic. On 22 August 1797 the Count Giuseppe Viscovich, Captain of Perast, lowered the Venetian war-flag of the Lion of Saint Mark pronouncing the farewell words in front of the crying people of the city and buried the "Gonfalon of Venice" under the altar of the main church of Perast.
The population has since decreased to 430 in 1910 and around 360 today. According to the "Comunita' nazionale italiana del Montenegro", in Perast actually there are 140 persons who still speak at home the original Venetian dialect of Perast (called "veneto da mar").
Musical styles
In some of the musical styles of Croatia it is quite evident that there was a merging of Slavic and Italian music. One such musical style that demonstrates this is Klapa music (klapa is an a cappella form of music - Venetian: clapa "singing crowd"). Klapa singing dates back centuries. The arrival of the Croatians to Dalmatia and their subsequent settlement in the area, began the long process of the cultural mixing of Slavic culture with that of the traditions of the Roman-Latin population of Dalmatia.
The Klape appeared in the coastal and island regions of Dalmatia. In the 19th century a standard form of Klapa singing emerged. The traditional Klapa was composed of up to a dozen male singers (in recent times there are also female Klape groups). Church music heavily influences the arrangements of this music giving it the musical form that exists today.
Perspectives on Dalamtia
Sir John Gardner Wilkinson
Sir John Gardner Wilkinson (1797 – 1875) was an English traveller, writer and pioneer Egyptologist of the 19th century. He is often referred to as "the Father of British Egyptology". He was in Dubrovnik (then called Ragusa) in 1848, he wrote in his; Dalmatia and Montenegro: With a Journey to Mostar in Herzegovina:
| “ | Italian is spoken in all the seaports of Dalmatia, but the language of the country is a dialect of the Slavonic, which alone is used by peasants in the interior.[33] | ” |
| “ | Their language though gradually falling into Venetianisms of the other Dalmatians towns, still retains some of that pure Italian idiom, for which was always noted. [34] | ” |
Andrew Archibald Paton
Andrew Archibald Paton (1811 - 1874) was a British diplomat and writer from the 19 century. In 1861 he wrote in his; Researches on the Danube and the Adriatic: Or, Contributions to the Modern:
| “ | ...the islands of Dalmatia owe much of their culture to the near vicinity of Venice and the more extensive use of the Italian language... [35] | ” |
Maude Holbach (a 1910 travel guide)
- Dalmatia-The Land Where East Meets West by Maude Holbach (a 1910 travel guide from COSIMO books and publications New York USA):
| “ | Two hundred years later that, is, early in the tenth century you might have heard Slavish and Latin spoken had you walked in the streets of Ragusa (Dubrovnik), just as you hear Slavish and Italian today ; for as times of peace followed times of war, the Greek and Roman inhabitants of Rausium intermarried with the surrounding Slavs, and so a mixed race sprang up, a people apart from the rest of Dalmatia. [36] | ” |
Zadar (Zara) during and after World War II
The chapter below is taken from the Secret Dalmatia Blog site, it is written by Alan Mandic.
| “ | The Italian majority in Zadar was first hurt by the Allied bombings and then chased away by the communist rule. In those terrible times, many people were looking for all sorts of revenges: from personal to national and many of Zadar’s Italians perished.[37][38] (Note: References added by Editor) Some say that bones of many are still in one of the caves of Levrnaka in Kornati, many managed to escape and leave their beloved city for good, some stayed and formed a small Italian community. Among those who went from their homes were Ottavio Missoni (fashion designer born in Dubrovnik). [39] | ” |
- Quote from the European Public Hearing on “Crimes Committed by Totalitarian Regimes":
| “ | Mystifying the crimes of the occupiers, Titoism covered its own crimes. The taboo to hide the crimes of Titoism was meant to conceal the War-time and post-War murders of civilians and prisoners of war without trials. Their graves were levelled and in Slovenia it was forbidden to talk about their fate. Repressive organs controlled the burials sites and the living were strictly forbidden to mention the victims or the graves. The so-called system of preserving and developing revolutionary heritage was used by the Communist Party to implement a monopoly on the truth. [40][41] | ” |
Individuals
- Roger Joseph Boscovich
- Benedetto Cotrugli
- Giovan Francesco Biondi
- Antonio Bajamonti
- Ottavio Missoni
See also
External links
References
- ^ Dalmatia (History, Culture, Art Heritage) by Antun Travirka (p137)
- ^ ""Dubrovnik." Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encyclopædia Britannica, 2011. Web. 08 Mar. 2011." (2011). Retrieved on 2011-03-8.
- ^ ""Croatia." Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encyclopædia Britannica, 2011. Web. 09 Mar. 2011." (2011). Retrieved on 2011-03-8.
- ^ Encyclopaedia Britannica (publ. 1911):
- ^ Dalmatia (History, Culture, Art Heritage) by Antun Travirka (p141)
- ^ Jews, Christians, and Muslims in the Mediterranean World after 1492 By Alisa Meyuhas Ginio (p190)
- ^ The Chicago Jewish forum, Volume 23 by Benjamin Weintroub (p271)
- ^ Footprint Croatia by Jane Foster (p271)
- ^ Croatia by Michael Schuman (p82)
- ^ When Ethnicity did not Matter in the Balkans: by John Van Antwerp Fine (p157)
- ^ The Fragmentation of Yugoslavia: Nationalism and War in the Balkans by Aleksandar Pavkovic.(p 47)
- The former Yugoslavia's political and cultural scene were heavily influenced by the cult of personality of the Dictator Josip Broz Tito.
- ^ Becoming Slav, Becoming Croat: Identity Transformations in Post-Roman and Early Medieval Dalmatia by Danijel Dzino (p43)
- ^ When Ethnicity did not Matter in the Balkans: by John Van Antwerp Fine (p11)
- ^ When Ethnicity did not Matter in the Balkans by John Van Antwerp Fine (p15)
- ^ Becoming Slav, Becoming Croat: Identity Transformations in Post-Roman and Early Medieval Dalmatia by Danijel Dzino (p20)
- ^ <templatestyles src="Module:Citation/CS1/styles.css"></templatestyles>""Yugoslavia." Genocide and Crimes Against Humanity. Ed. Dinah L. Shelton. Gale Cengage, 2005. eNotes.com. 2006. 24 Nov, 2010". 2010. Retrieved 2010-11-25. Check date values in:
|date=(help)- "Native German and Hungarian communities, seen as complicit with wartime occupation, were brutally treated; tantamount in some cases to ethnic cleansing. The Volksdeutsch settlements of Vojvodina and Slavonia largely disappeared. Perhaps 100,000 people—half the ethnic German population in Yugoslavia—fled in 1945, and many who remained were compelled to do forced labor, murdered, or later ransomed by West Germany. Some 20,000 Hungarians of Vojvodina were killed in reprisals. Albanian rebellions in Kosovo were suppressed, with prisoners sent on death marches towards the coast. An estimated 170,000 ethnic Italians fled to Italy in the late 1940s and 1950s. (All of these figures are highly approximate.)"
- ^ The Frontiers of Europe by Malcolm Anderson & Eberhard Bort (p77)
- ^ History in Exile: Memory and Identity at the Borders of the Balkans by Pamela Ballinger (p155)
- ^ A London Encyclopaedia: Or Universal Dictionary of Science, Art, Literature (p48)
- "In the latter ages of the Roman Empire this country suffered frequently from in-roads of Barbarians..."
- ^ The Changing Face of Dalmatia: Archaeological and Ecological Studies in a Mediterranean landscape by John Chapman, Robert Shiel & Sime Batovic
- "In chapters 29 and 30, two similar accounts are given for the fall of nearby Salona to the Avars and Slavs ..."
- ^ The Italians of Dalmatia: From Italian Unification to World War One by Luciano Monzali (p5)
- ^ Becoming Slav, Becoming Croat: Identity Transformations in Post-Roman and Early Medieval Dalmatia by Danijel Dzino (p212).
- ^ Becoming Slav, Becoming Croat: Identity Transformations in Post-Roman and Early Medieval Dalmatia by Danijel Dzino (p52).
- ^ The Illyrians by John Wilkes (p269)
- ^ Dalmatian Language-Dictionary
- ^ Encyclopedia of the Languages of Europe by Glanville Price (p377)
- ^ University College London, School of Slavonic and East European Studies The Slavonic and East European Review-The Slavonic Latin Symbiosis in Dalmatia during the Middle Ages by Victor Novak
- ^ <templatestyles src="Module:Citation/CS1/styles.css"></templatestyles>"Encyclopaedia Britannica (1911 Edition): Orography". 2010. Retrieved 2010-11-22. Check date values in:
|date=(help)- "OROGRAPHY: That part of physical geography which deals with the geological formation, the surface features and description of mountains. The terms "oreography," "orology" and "oreology" are also sometimes used.
- ^ Earthquake Monitoring and Seismic Hazard Mitigation in Balkan Countries by Eystein Sverre Husebye (p86)
- ^ The Extraterrestrial Life Debate, 1750-1900 by Michael J. Crowe (p.156)
- ^ The Hvar Rebellion (1510 - 1514) was an uprising of the people and citizens of the Venetian Dalmatia island of Hvar against the island's nobility and their Venetian masters.
- ^ The Italians of Dalmatia: From Italian Unification to World War One by Luciano Monzali (p8)
- ^ Dalmatia and Montenegro: With a journey to Mostar in Herzegovina.Volume 1 by Sir John Gardner Wilkinson (p4)
- ^ Dalmatia and Montenegro: With a journey to Mostar in Herzegovina.Volume 1 by Sir John Gardner Wilkinson (p362)
- ^ Researches on the Danube and the Adriatic, Volume 1 by Andrew Archibald Paton (p167)
- ^ Dalmatia: The Land Where East Meets West by Maude Holbach (p121)
- "DALMATIA: The Land Where East Meets West is MAUDE M. HOLBACH's second book of travel in Eastern Europe. First published in 1910, this is an anthropological travel journal of an often-overlooked kingdom" Web site: www.cosimobooks.com
- ^ Refugees in the Age of Total War by Anna Bramwell (p136, read Zara-p137)
- ^ A Tragedy Revealed The Story of the Italian Population of Istria & Dalmatia by Arrigo Petacco. (p12 & read page 81 Zadar/Zara)
- ^ <templatestyles src="Module:Citation/CS1/styles.css"></templatestyles>"Zadar – The postcards from the past". 2010. Retrieved 2010-11-25. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ^ European Public Hearing on “Crimes Committed by Totalitarian Regimes" (p201)
- ^ European EU's press releases concerning European Public Hearing on: “Crimes Committed by Totalitarian Regime-Brussels"
<sharethis />